Open Access Week
Open Access Week, a global event now entering its fifth year, is an opportunity for the academic and research community to continue to learn about the potential benefits of Open Access, to share what they’ve learned with colleagues, and to inspire wider participation in helping to make Open Access a new norm in scholarship and research. Open access to information – the free, immediate, online access to the results of scholarly research, and the right to use and re-use those results as you need – has the power to transform the way research and scientific inquiry are conducted. It has direct and widespread implications for academia, medicine, science, industry, and for society as a whole.
During the week of October 24-30, the Northeastern University Libraries will host a series of events to celebrate Open Access. The events will cover a range of topics:
- open collaboration in the sciences
- the effects of Wikipedia and social networking on student research
- open access works by Northeastern faculty
- free and open college textbooks
- data gathering and storage needs of grad students
⇒ Click here to view the full schedule of events for Open Access Week.
The Library has supported Open Access in the Northeastern community since 2006 in the form of the University’s digital archive,
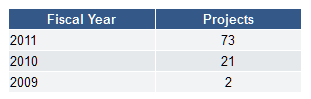
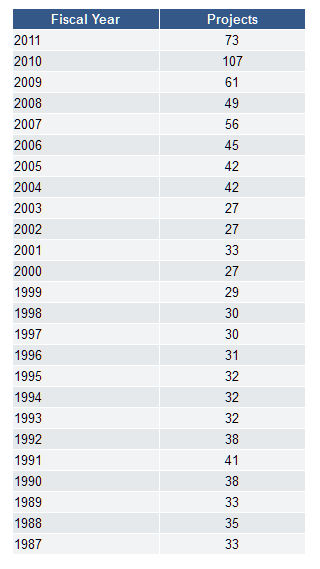
IRis. The goal of IRis is to collect, manage, preserve, and share the intellectual output and historical record of Northeastern University. IRis provides open access to NU researchers who want to promote and preserve their materials, to NU students who require digital storage and promotion of their dissertations and theses, to NU administrators who need to save important university records, and to anyone who is seeking information on the intellectual productivity of the Northeastern community. Since its start, IRis has expanded to hold 531 faculty publications and approximately 600 dissertations and master’s theses. And since January 1, 2010, there have been over 230,000 downloads of full-text items from IRis, which include scholarly content as well as university archival content.
Building upon the success of IRis, the Library will soon offer a robust digital repository and preservation service to the campus for digital collections, images, media, and data, as well as accompanying metadata and consulting help.
 Open Access Week, a global event now entering its fifth year, is an opportunity for the academic and research community to continue to learn about the potential benefits of Open Access, to share what they’ve learned with colleagues, and to inspire wider participation in helping to make Open Access a new norm in scholarship and research. Open access to information – the free, immediate, online access to the results of scholarly research, and the right to use and re-use those results as you need – has the power to transform the way research and scientific inquiry are conducted. It has direct and widespread implications for academia, medicine, science, industry, and for society as a whole.
During the week of October 24-30, the Northeastern University Libraries will host a series of events to celebrate Open Access. The events will cover a range of topics:
Open Access Week, a global event now entering its fifth year, is an opportunity for the academic and research community to continue to learn about the potential benefits of Open Access, to share what they’ve learned with colleagues, and to inspire wider participation in helping to make Open Access a new norm in scholarship and research. Open access to information – the free, immediate, online access to the results of scholarly research, and the right to use and re-use those results as you need – has the power to transform the way research and scientific inquiry are conducted. It has direct and widespread implications for academia, medicine, science, industry, and for society as a whole.
During the week of October 24-30, the Northeastern University Libraries will host a series of events to celebrate Open Access. The events will cover a range of topics: