The following is a series written by archivists, academics, activists, and educators making available primary source material, providing pedagogical support, and furthering the understanding of Boston Public School’s Desegregation history.
Guest Post by Elizabeth Coup
Throughout the summer and fall of 2016, I am working with Northeastern University’s Archives and Special Collections and more specifically their portion of the materials that have been scanned for the Boston Public Schools Desegregation Project, creating EAC-CPF (Encoded Archival Context – Corporate Bodies, Persons, and Families) records. I am doing this work as part of an independent study for the Simmons College Library and Information Science master’s program, culminating more than two years of practical and intellectual study with this project, which is supervised by Katherine Wisser, Chair of the Society of American Archivists EAC Working Group.
Coming into the program at Simmons, I had a master’s from New York University’s Institute of Fine Arts in art and architectural history and several years as a sports journalist, thus an interest in written analysis and description was long engrained. Discovering archival standards for description and encoding description only furthered this focus, and the relationship between entities (who might also be creators) and archival materials or records struck me from the moment I heard of it. In the ensuing years of coursework and as an early professional processing collections at the Phillips Library, Peabody Essex Museum, and at the Center for the History of Medicine, where I am presently a processing assistant, this interest only expanded. How do we think about the records we arrange and describe? How do we make the choices for describing them? And then, on the other hand, how do we describe the entities that are related to the record—but also might be related to one another? How does describing entities and relationships between them improve access to archival materials? It is these final questions that I am exploring with my ongoing project.
In fall 2015, I met with Giordana Mecagni, the Head of Northeastern University’s Archives and Special Collections, for a project that was part of my regular coursework in the Simmons College Library and Information Sciences master’s program. During our conversation, she told me about the Boston Public Schools Desegregation Project, which immediately struck me for multiple reasons, one of which was that it might be just the project for which encoded description specific to creators, rather than materials, might be extremely useful. It is a significantly sized online collection not just from Northeastern’s archives, but also across multiple local and regional archives, and with a range of creators that spans from national and regional political figures to lesser known activists and neighborhood organizations. Thinking about describing the relationships between these creators—or entities—as well as providing users with access to additional description not of materials, but of entities, became the impetus for this project.
The project began this past summer, when I began working with Giordana Mecagni, Michelle Romero, and Daniel Jergovic to create an EAC-CPF template that could be used not only for entities related to this project, but also for all entities related to Northeastern collections. Furthermore, I established a list of all primary entities associated with the BPS Desegregation Project materials at Northeastern, and then met with Giordana and Michelle to prioritize a group for which records would be created first. The ways to think about prioritizing came from two directions: the importance of the entities within the historical context of BPS Desegregation and relevance to Northeastern’s archival holdings. Considering these concepts, we came to a list of some thirty-two entities, which range from members of government and national social justice organizations to neighborhood groups and local activists, and I stepped into the biographical research portion of the project.
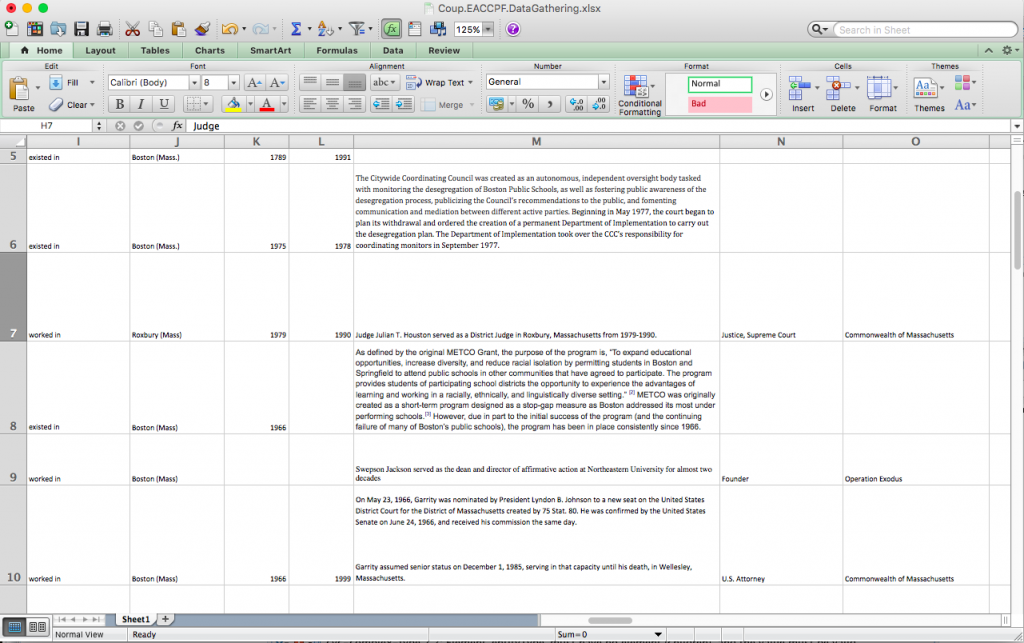
Simultaneously, we began the process of reviewing the EAC-CPF template I created, based on examples from other locations exploring the standard, such as “Connecting the Dots,” a Yale-Harvard collaboration relating to describing lexicographer Samuel Johnson and his circle, and those who collected their materials, as well as the Field Book Project at the Smithsonian Institute Archives. I also looked at the more open and flexible templates being created at present for institution-wide usage at Harvard Libraries, including the Center for the History of Medicine, which is in the process of creating a template and defining guidelines at the present. With these in mind, I created a sample entry, which has then been adapted and edited through email exchanges and meeting with Northeastern staff and Kathy Wisser. We hope to have that template solidified in the coming weeks, so that I can begin producing records for those priority entities.
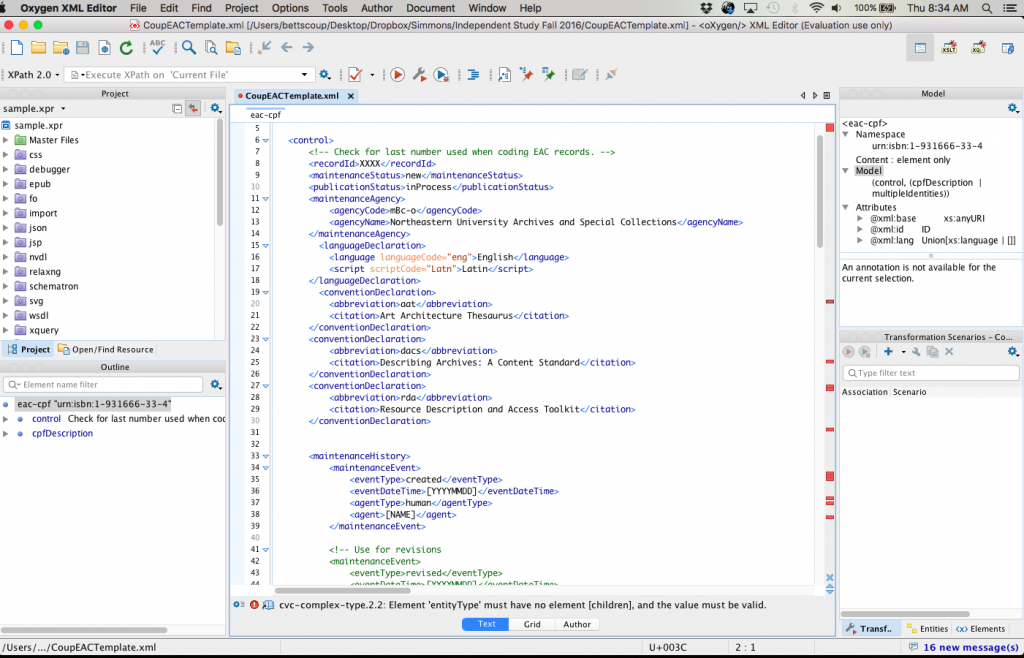
Perhaps the most challenging (and interesting) consideration throughout the research and template creation stages is the concept that EAC does not in fact describe archival materials, but the entities themselves. For these reasons, LCSH subject headings make less sense to describe the entities than, say, occupations authorities. When writing biographical or historical notes, the note is not exactly what one might create for a finding aid; it is not related to the materials in the collection but to the entities’ entire biography or history. What we as archivists write for finding aids might be just one chapter of what should appear in an EAC-CPF record. Still, the hope is that EAC records provide better access not just to the entity, but to archival materials, both created by this entity and by entities that might be related to this individual or corporate body, also described in EAC-CPF records. In a blogpost describing the Field Book Project at the Smithsonian, Tammy Peters wrote, “EAC-CPF helps outline an historical social network. Not only can a researcher find links to materials from that one person for whom they started their search, but they can also find resources concerning the organizations and people associated with that person.”[1] Thus, though one is describing an entity—a person, corporate body, or family—one is doing so within the context of archival description.
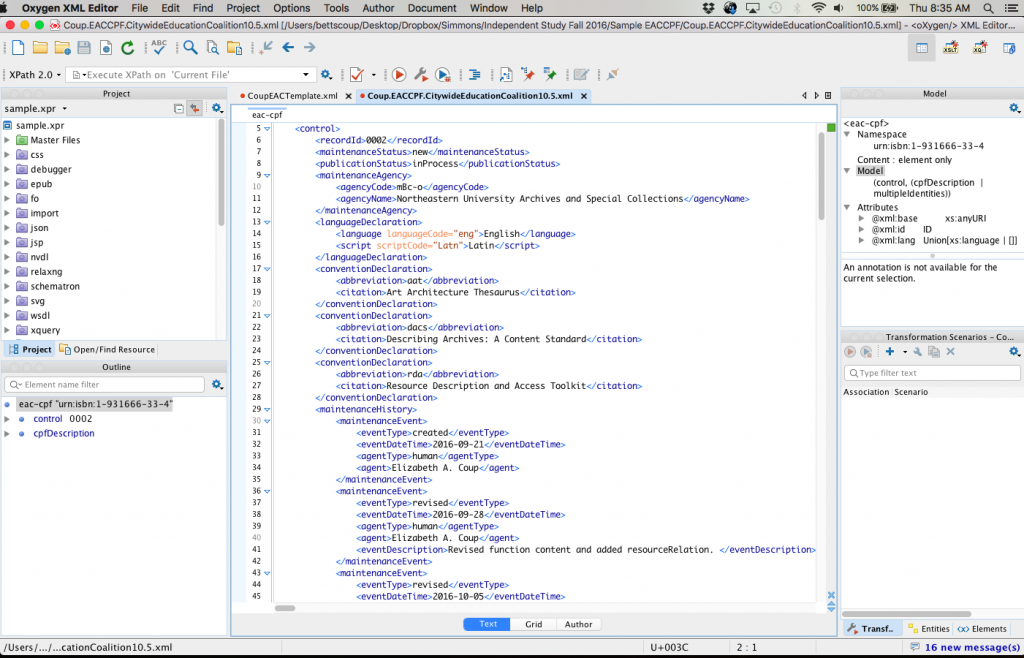
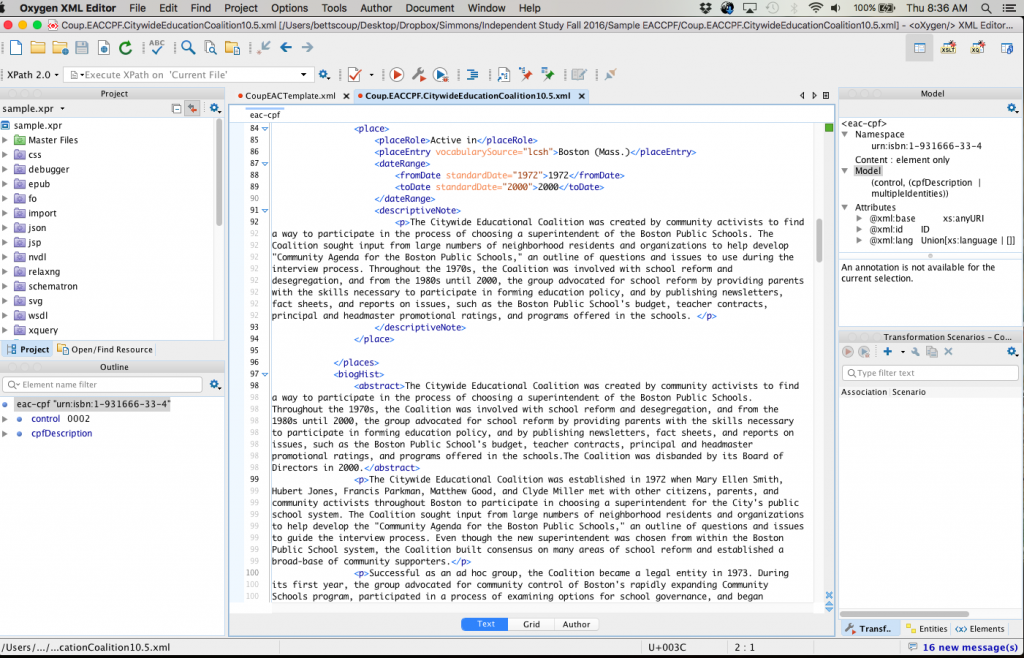
The challenge, of course, with using a new standard, is to make it work specifically for an institution and its needs, and to understand how best to do that. Within the project, I am working closely with Northeastern staff and Kathy Wisser to ensure that we not only create useful records that provide improved user access to archival materials, but also create best practice guidelines and a template which archivists, student workers and interns can all use going forward. Thus, the project is not just one that lasts a bit longer than a semester, but instead creates practice that will move into the future with Northeastern’s Archives and Special Collections.
[1] Peters, Tammy, “Historical Context and Connections,” http://nmnh.typepad.com/fieldbooks/2012/09/historical-context-and-connections.html
