Box By Box: Inventorying the Boston Globe Big Dig Records
The Big Dig, a major infrastructure project that aimed to improve traffic flow, dominated the Boston area throughout its construction for 15 years and led to countless articles and columns in the Boston Globe. Former Globe reporters and editors Tom Palmer and Sean Murphy, who both worked at the newspaper for over 30 years, donated their extensive records to the Northeastern University Archives and Special Collections, providing a glimpse into the planning and construction of the Big Dig project. (NUASC holds multiple other collections relating to the Big Dig, as well.)

The initial planning of the Big Dig, officially named the Central Artery/Tunnel Project, began in 1982 and actual construction occurred from 1991-2006. The donated records contained articles by both Palmer and Murphy, as well as a third reporter, Charles Sennott.
I find this collection interesting because it is not just a compilation of articles published in the Boston Globe; it consists of the research and reference materials amassed for use in reporting on the issues surrounding the Big Dig. The records reveal the vast context and information a journalist would need to know in order to write cohesive articles, including contracts, technical reports, financial statements, photographs, maps, articles from other news sources, and more.
Below are some selected items to highlight the extent of the collection.
Big Dig Contract Map
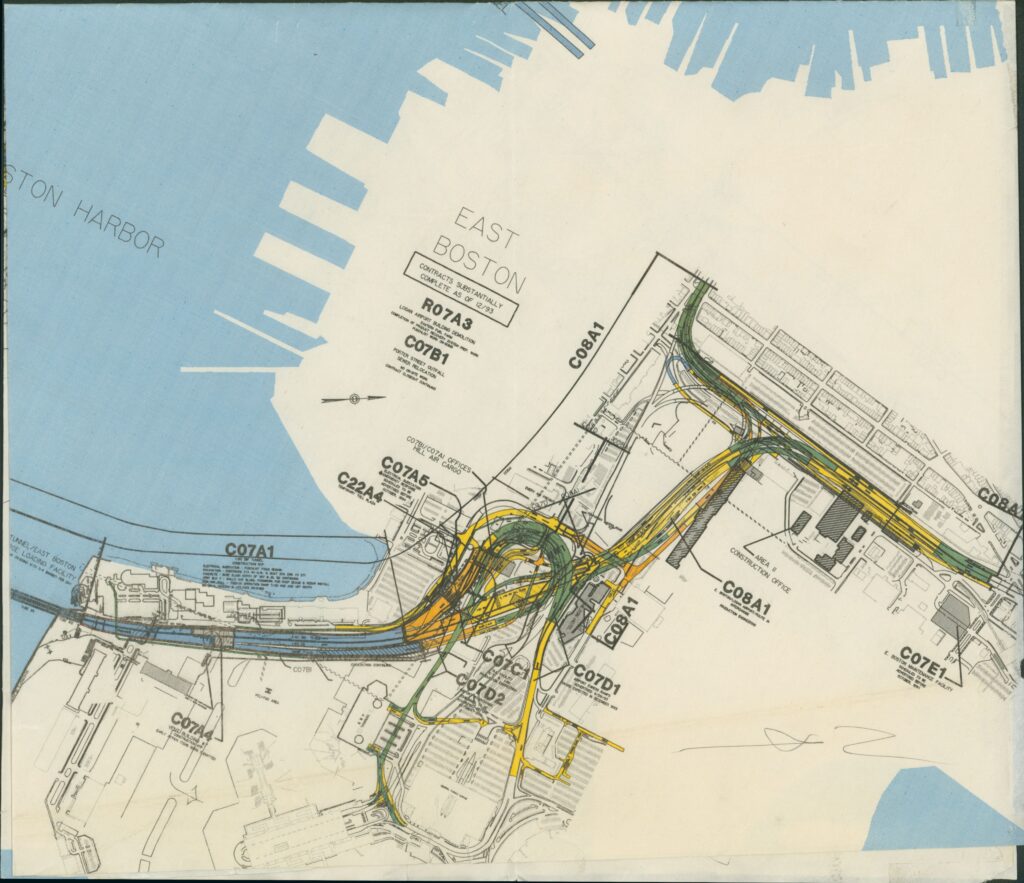
The contracts in progress map is a snapshot of the various contracts happening at one time in downtown Boston and serves as a great visualization of the contracts’ physical locations. It also helps associate the technical contract number with the more publicly known name of any given section of the project, such as the Ted Williams Tunnel identified as contract number C07A1.
The Big Dig Blame Game

As Massachusetts Governor from 1997-2001, Paul Cellucci was the subject of countless voiced opinions about his tenure and leadership during the Big Dig project. This image of Cellucci as a snake accompanied an article published in a 2000 issue of Boston Magazine that suggested cost overruns were caused by a collective failure of key players, including Cellucci, for not properly managing the project.
A Fifth-Grader’s Opinion on the Big Dig

Often stuck in traffic with their parents or simply by living in nearby neighborhoods, local students were also affected by the Big Dig project. The Student Newsline section in the Boston Globe presented an opportunity for students to send in their own opinions about the project. Many students offered their own ideas to quickly finish and reduce the costs of the project.
2006 Ceiling Collapse
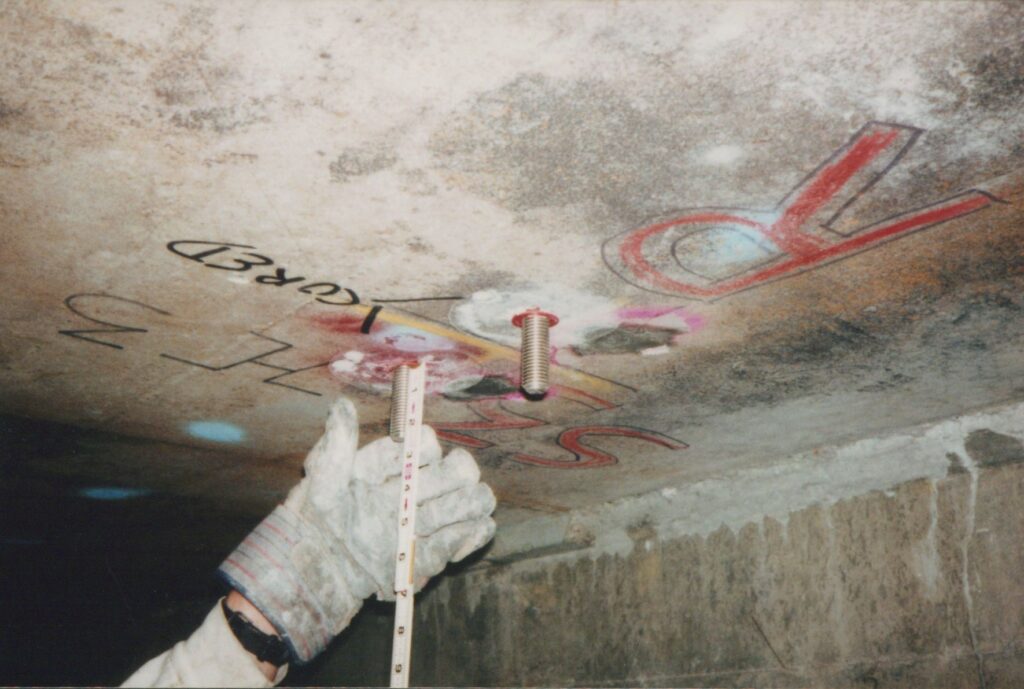
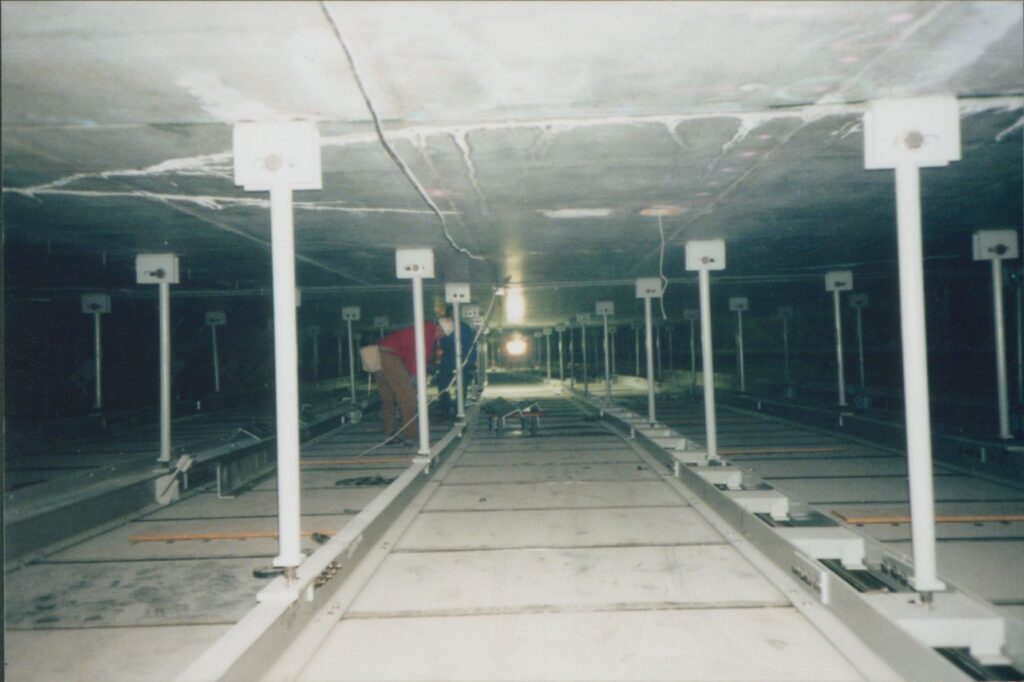


Reporting on the construction of the Big Dig included documenting tragedies. In 2006, a ceiling panel fell on a car in the Fort Point Channel Tunnel, killing a passenger and injuring the driver. Their family and the public wanted answers as to how the incident could have occurred. As a result, the Boston Globe undertook an in-depth investigation to report and provide answers. These photographs may have been taken to document the other ceiling panels in the rest of the tunnel after the accident occurred.
To learn more about accessing the Boston Globe Big Dig records, email the Northeastern University Archives and Special Collections at archives@northeastern.edu.
Aries Peralta (he/him) recently graduated from Simmons University with an MS in Library and Information Science with a concentration in archives management. He received his BA in history from the University of Connecticut.













